Imitation game

Last month we had the pleasure of hosting artist and scientist Dr Immy Smith as part of her week-long takeover of @IAmSciArt on Twitter. Drawing inspiration from the Museum’s collections, Immy has created some beautiful paintings. Here she tells us a little more about her interests and work…
My current artwork is focused on crypsis and mimicry – the ways that animals and plants disguise themselves or pretend to be something they’re not. Cryptic camouflage helps animals to avoid being seen, often to help them catch prey – or to avoid becoming prey themselves! Mimicry is also often about trying not to get eaten: the harmless hornet moth, for example, mimics a stinging insect to deter predators. I use these themes to develop print art projects, and also public workshops to help people learn more about the ecology of cryptic animals.

In my arts practice I try to imagine how animals and plants might evolve to camouflage themselves on human-made materials, and what they might look like. Will we one day find moths adapted to hide on advertising hoardings, or beetles mimicking litter? I made an entire deck of Cryptic Cards as a response to this kind of question.
Another project I’m working on at the moment is called Emergent Crypsis. This is a collaboration with Norweigan generative artist Anders Hoff who makes art using algorithms executed by a computer. I’m imagining how creatures might adapt to an extreme example of human-made patterns – computer generated abstract images.

My work requires me to closely study many animals and plants, but how do I learn about all these species in order to draw their imaginary relatives? How do I make my art a convincing representation of how life might find ways to hide on human-made art?
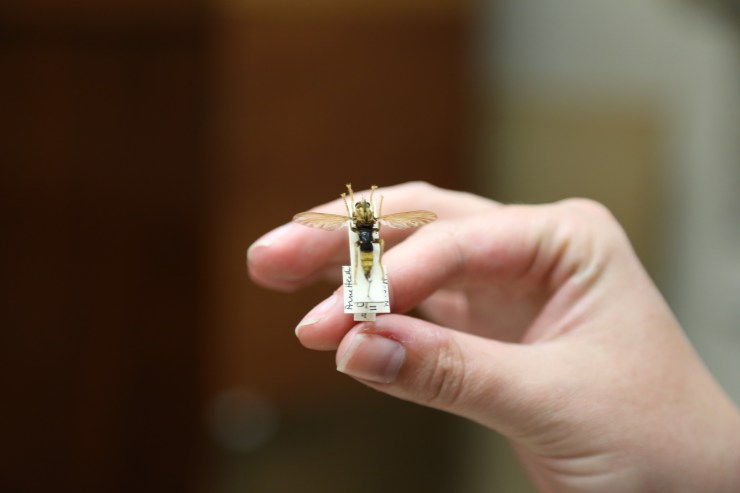
One answer is of course, the internet. I’ve been lucky enough to find many wildlife photographers online who are kind enough to let me use their images as reference. But photographs alone are not always enough to get to know the fine details and defining characteristics of a species: the joints and articulations of small insects, for example, are best studied from specimens. And some species are rare, or even extinct, and it can be hard to find photographic a reference.

This is where scientific collections come into the picture. The collections held in museums and other institutions are not only essential for scientists and scientific illustrators, they are also an invaluable resource for artists of many disciplines, science communicators, and educators of many kinds. In the collections at the Oxford University Museum of Natural History I can photograph and sketch leaf-mimicking insects, for example, that are native to the forests of South America which I may never visit. I can study in minute detail the articulation of beetles that are rarely seen, and which might be difficult to find – and irresponsible to collect – myself.

Not only do I find specific species that I want to study in natural history collections, I often see new ones – animals I didn’t know about or hadn’t thought of drawing before. In the same week that I visited Oxford, I also made a trip to Herbarium RNG in Reading to study plant mimicry, and found similar inspiration there. I can channel all this into both aesthetic art destined for print and sciart workshops that communicate the wonders of insects or plants with the wider community.
Working on sciart projects and educational workshops helps me appreciate the multitude of ways in which collections benefit research and education. We must try to communicate the plethora of roles they play, and the host of ways they cross into our lives – whether through scientific research on insects pollinators of the crops we eat, or via a deck of cards made by someone like me for mainly recreational purposes. We must fight to protect scientific collections because they are a resource that benefits all of us as a society.